先来一个简单LVM磁盘空间扩展的例子。
1. Verify the size of Logical Volume:
2. Verify the Size on mounted directory:
3. Use :
4. Again Verify using lvdisplay
下面这个是LVM在线扩展磁盘的详细实例,好不容易找到的,分享给大家。
1、添加磁盘,连接至主机。开机,进入系统。使用root登录,运行fdisk,将新加的磁盘分区
[root@jbxue ~]# fdisk –l
Disk /dev/hda: 6442 MB, 6442450944 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 783 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/hda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux
/dev/hda2 14 783 6185025 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/hdb: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes
16 heads, 63 sectors/track, 4161 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 1008 * 512 = 516096 bytes
Disk /dev/hdb doesn't contain a valid partition table
[root@jbxue ~]# fdisk /dev/hdb
Command (m for help): n //创建分区
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-4161, default 1): 1
Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (1-4161, default 4161):
Using default value 4161
Command (m for help): p //查看分区
Disk /dev/hdb: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes
16 heads, 63 sectors/track, 4161 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 1008 * 512 = 516096 bytes
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/hdb1 1 4161 2097112+ 83 Linux
Command (m for help): t //更改ID值(LVM卷为:8e)
Selected partition 1
Hex code (type L to list codes): 8e
Command (m for help): w //保存退出
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
[root@jbxue ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/hda: 6442 MB, 6442450944 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 783 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/hda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux
/dev/hda2 14 783 6185025 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/hdb: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes
16 heads, 63 sectors/track, 4161 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 1008 * 512 = 516096 bytes
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/hdb1 1 4161 2097112+ 8e Linux LVM
2、创建PV
3、扩展VG
运行vgdisplay ,查看扩展后的VG,如果显示容量增加,表示,VG扩展成功
4、扩展LV
5、激活VG
6、调整文件系统大小
[root@jbxue ~]# e2fsck -a /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 //调整前先检查下文件系统
/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 is mounted.
WARNING!!! Running e2fsck on a mounted filesystem may cause
SEVERE filesystem damage.
Do you really want to continue (y/n)? y
/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00: recovering journal
/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00: Clearing orphaned inode 786561 (uid=500, gid=500, mode=0100600, size=0)
/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00: Clearing orphaned inode 786556 (uid=500, gid=500, mode=0100600, size=0)
/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00: Clearing orphaned inode 786554 (uid=500, gid=500, mode=0100600, size=0)
/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00: Clearing orphaned inode 786436 (uid=500, gid=500, mode=0100600, size=0)
/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00: Clearing orphaned inode 786435 (uid=500, gid=500, mode=0100600, size=0)
/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00: clean, 123302/1277952 files, 823124/1277952 blocks
[root@jbxue ~]# resize2fs /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00
------------------------------------------------
resize2fs 1.39 (29-May-2006)
Filesystem at /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 is mounted on /; on-line resizing required
Performing an on-line resize of /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 to 1777664 (4k) blocks.
The filesystem on /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00 is now 1777664 blocks long.
在线扩容完成!
附1、LVM介绍
LVM(Logicl Volume Manager),逻辑卷管理器,通过使用逻辑卷管理器对硬盘存储设备进行管理,可以实现硬盘空间的动态划分和调整。
结构图:
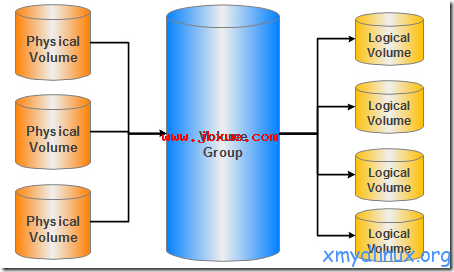
物理卷-----PV(Physical Volume)
物理卷在逻辑卷管理中处于最底层,它可以是实际物理硬盘上的分区,也可以是整个物理硬盘。
卷组--------VG(Volumne Group)
卷组建立在物理卷之上,一个卷组中至少要包括一个物理卷,在卷组建立之后可动态添加物理卷到卷组中。一个逻辑卷管理系统工程中可以只有一个卷组,也可以拥有多个卷组。
逻辑卷-----LV(Logical Volume)
逻辑卷建立在卷组之上,卷组中的未分配空间可以用于建立新的逻辑卷,逻辑卷建立后可以动态地扩展和缩小空间。系统中的多个逻辑卷要以属于同一个卷组,也可以属于不同的多个卷组。
附2、lvm常用管理工具: