通过update-rc.d、rc.local管理ubuntu开机启动
测试环境:ubuntu10.04 && ubuntu12.04
ubuntu系统运行级别:
0 系统停机状态
1 单用户或系统维护状态
2~5 多用户状态
6 重新启动
update-rc.d概要
linux services can be started, stopped and reload with the use of scripts stocked(贮存) in/etc/init.d/. However, during start up or when changing runlevel, those scripts are searched in /etc/rcX.d/ where X is the runlever number(可以用runlevel命令查看系统默认的runlevel). This tutorial will explain how one can activate(激活), disactivate or modifu a service start up. When installing a new service under debian, the default is to enable it. So for instance, if you just installed apache2 package, after you installed it, apache service will be started and so will it be upon the next reboots. If you do not use apache all the time, you might want to disable this service from starting up upon boot up and simply start it manually when you actually need it by running this command:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 start
You could either disable this service on boot up by removing any symbolic links in /etc/rcX.d/SYYapache2 or by using update-rc.d.The advantage of using update-rc.d is that is will take care of removing/adding any required links to /etc/init.d automatically.Taking apache2 as an example.
As you can see, for runlevels 0, 1 and 6 there is a K at the begining of the link, for runlevels 2, 3, 4 and 5, there is a S. Those two letters stands for Kill and Start.
Removing A Service
If you want to totally disable apache2 service by hand, you would need to delete every single link in /etc/rcX.d/. Using update-rc.d it is a simple as :
update-rc.d [-f] servicename remove
Option -f Force removal of symlinks even if /etc/init.d/name still exists.(相当于就算/etc/init.d/下还存在apache脚本,但是/etc/rcX.d/下所有关于apache2的软链接均被删除)
Adding A Service
Default Priorities
Now, if you want to re-add your service to be started on boot up, you can simply use:
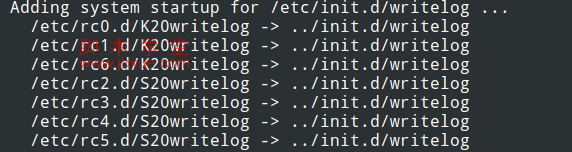
Specifying Custom Runlevels
Finally, if you want to Start and Kill on Specific runlevels, like for instances starting writelog with priority 90 on runlevels 2, 3, 4, 5 and kill with priority 91 on runlevels 0, 1 and 6, you can follows this operation:
init.d启动脚本:
第二种方法,rc.local设置开机启动。
首选,查看rc.local文件的运行权限和运行level级别:
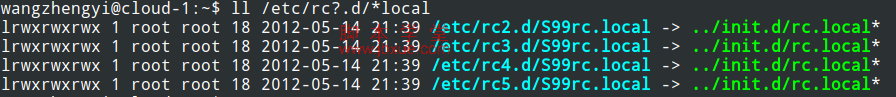
可以看出,rc.local运行在runlevel为2,3,4,5,并且运行优先级为99,也就是最低的优先级,因此也可以把需要开机启动的脚本加入到rc.local中:
linux开机启动的方法,第一种update-rc.d管理,灵活性更高,并可以解决相关依赖,需要熟悉linux开机启动流程,更容易掌握这块的内容。