在计算机图形用户界面中,拖放(drag-and-drop)是指点击某个虚拟对象,并拖动到一个不同的位置或者到另一个虚拟对象上的操作.
通常,它可以用来激活很多类型的操作,或是在两个抽象对象之间创建各种不同的关联.
专题:wxpython中文教程
一个wxPython实现的拖动例子:
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding=utf-8
#dragdrop.py
import os
import wx
class MyTextDropTarget(wx.TextDropTarget):
def __init__(self, object):
wx.TextDropTarget.__init__(self)
self.object = object
def OnDropText(self, x, y, data):
self.object.InsertStringItem(0, data)
class MyFrame(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self, parent, id, title):
wx.Frame.__init__(self, parent, id, title,
wx.DefaultPosition, wx.Size(450, 400))
splitter1 = wx.SplitterWindow(self, -1, style=wx.SP_3D)
splitter2 = wx.SplitterWindow(splitter1, -1, style=wx.SP_3D)
self.dir = wx.GenericDirCtrl(splitter1, -1, dir='/home/',
style=wx.DIRCTRL_DIR_ONLY)
self.lc1 = wx.ListCtrl(splitter2, -1, style=wx.LC_LIST)
self.lc2 = wx.ListCtrl(splitter2, -1, style=wx.LC_LIST)
dt = MyTextDropTarget(self.lc2)
self.lc2.SetDropTarget(dt)
wx.EVT_LIST_BEGIN_DRAG(self, self.lc1.GetId(), self.OnDragInit)
tree = self.dir.GetTreeCtrl()
splitter2.SplitHorizontally(self.lc1, self.lc2)
splitter1.SplitVertically(self.dir, splitter2)
wx.EVT_TREE_SEL_CHANGED(self, tree.GetId(), self.OnSelect)
self.OnSelect(0)
self.Center()
def OnSelect(self, event):
list = os.listdir(self.dir.GetPath())
self.lc1.ClearAll()
self.lc2.ClearAll()
for i in range(len(list)):
if list[i][0] != '.':
self.lc1.InsertStringItem(0, list[i])
def OnDragInit(self, event):
text = self.lc1.GetItemText(event.GetIndex())
tdo = wx.PyTextDataObject(text)
tds = wx.DropSource(self.lc1)
tds.SetData(tdo)
tds.DoDragDrop(True)
class MyApp(wx.App):
def OnInit(self):
frame = MyFrame(None, -1, 'dragdrop.py')
frame.Show(True)
self.SetTopWindow(frame)
return True
app = MyApp(0)
app.MainLoop()
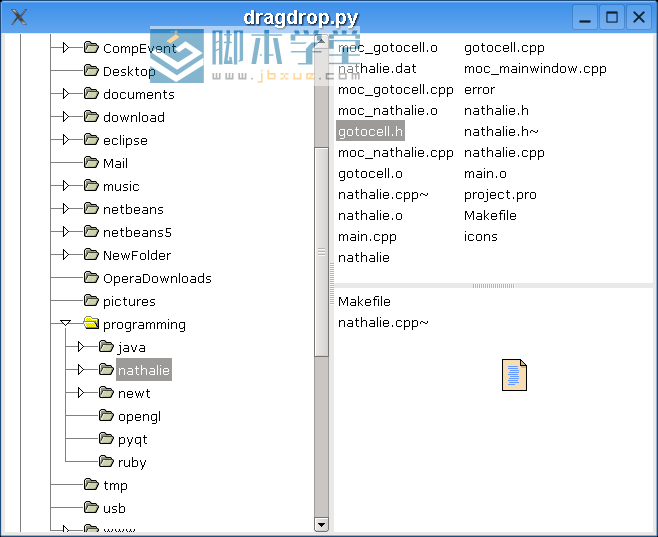
图:dragdrop.py
GUI比起控制台的优势之一就是其直观性(intuitiveness). 你在学习一个GUI程序时会比控制台程序跟容易. 通常无需手册.
而另一方面,一些图形化操作又是过于复杂,比如以拖动方式将文件扔到垃圾桶是非常直观易于理解的,但事实上大多数人只是按下删除键. 当然通过shift+delete是更管用的.
例2,发掘另一个图形化操作, 那可真是很便利的.
在大多数GUI文本编辑器中,都能够通过简单地从文件管理器中拖入一个文件来打开它.
代码:
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding=utf-8
#filedrop.py
# www.plcxue.com
import wx
class FileDrop(wx.FileDropTarget):
def __init__(self, window):
wx.FileDropTarget.__init__(self)
self.window = window
def OnDropFiles(self, x, y, filenames):
for name in filenames:
try:
file = open(name, 'r')
text = file.read()
self.window.WriteText(text)
file.close()
except IOError, error:
dlg = wx.MessageDialog(None,
'打开以下文件时遇到错误:n'+str(error))
dlg.ShowModal()
except UnicodeDecodeError, error:
dlg = wx.MessageDialog(None,
'不能打开非 ascii 文件n'+str(error))
dlg.ShowModal()
class MyFrame(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self, parent, id, title):
wx.Frame.__init__(self, parent, id, title,
wx.DefaultPosition, wx.Size(450, 400))
self.text = wx.TextCtrl(self, -1, style = wx.TE_MULTILINE)
dt = FileDrop(self.text)
self.text.SetDropTarget(dt)
self.Center()
class MyApp(wx.App):
def OnInit(self):
frame = MyFrame(None, -1, 'filedrop.py')
frame.Show(True)
self.SetTopWindow(frame)
return True
app = MyApp(0)
app.MainLoop()